python查询MySQL写入Excel
发布时间:2020-05-13 14:42:59编辑:admin阅读(3630)
一、概述
现有一个用户表,需要将表数据写入到excel中。
环境说明
mysql版本:5.7
端口:3306
数据库:test
表名:users
表结构如下:
CREATE TABLE `users` ( `id` bigint(20) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `username` varchar(50) COLLATE utf8mb4_bin NOT NULL COMMENT '用户名', `password` varchar(255) CHARACTER SET utf8mb4 DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '密码', `phone` varchar(20) CHARACTER SET utf8mb4 DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '手机号', `email` varchar(255) CHARACTER SET utf8mb4 DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '邮箱', `create_time` datetime DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP COMMENT '创建时间', PRIMARY KEY (`id`) ) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4 COLLATE=utf8mb4_bin;
插入3行数据
INSERT INTO `test`.`users` (`id`, `username`, `password`, `phone`, `email`, `create_time`) VALUES ('1', 'xiao', '123', '12345678910', '123@qq.com', '2020-04-10 01:22:07');
INSERT INTO `test`.`users` (`id`, `username`, `password`, `phone`, `email`, `create_time`) VALUES ('2', 'zhang', '123', '12345678910', '123@qq.com', '2020-04-10 01:22:07');
INSERT INTO `test`.`users` (`id`, `username`, `password`, `phone`, `email`, `create_time`) VALUES ('3', 'lisi', '123', '12345678910', '123@qq.com', '2020-04-10 01:22:07');
二、基本写法
安装模块
pip3 install xlwt pymysql
test_excel.py
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# coding: utf-8
import os
import xlwt
import pymysql
import datetime
class MysqlToExcel(object):
def __init__(self):
self.host = '10.212.21.92'
self.user = 'root'
self.passwd = 'abcd1234'
self.db_name = 'test'
self.port = 3306
self.file_name = 'data.xls'
def get_query_results(self):
sql = "select * from test.users"
conn = pymysql.connect(
host=self.host,
user=self.user,
passwd=self.passwd,
port=self.port,
database=self.db_name,
charset='utf8',
cursorclass=pymysql.cursors.DictCursor
)
cur = conn.cursor() # 创建游标
cur.execute(sql) # 执行sql命令
result = cur.fetchall() # 获取执行的返回结果
# print(result)
cur.close()
conn.close() # 关闭mysql 连接
return result
def generate_table(self):
"""
生成excel表格
:return:
"""
# 删除已存在的文件
if os.path.exists(self.file_name):
os.remove(self.file_name)
result = self.get_query_results()
# print(result)
if not result:
print("查询结果为空")
return False
# 创建excel对象
f = xlwt.Workbook()
sheet1 = f.add_sheet('Sheet1', cell_overwrite_ok=True)
# 列字段
column_names = ['id','username','password','phone','email']
# 写第一行,也就是列所在的行
for i in range(0, len(column_names)):
sheet1.write(0, i, column_names[i])
# 写入多行
num = 0 # 计数器
for i in result:
sheet1.write(num + 1, 0, i['id'])
sheet1.write(num + 1, 1, i['username'])
sheet1.write(num + 1, 2, i['password'])
sheet1.write(num + 1, 3, i['phone'])
sheet1.write(num + 1, 4, i['email'])
# 日期转换为字符串
value = i['create_time'].strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S')
sheet1.write(num + 1, 5, value)
num += 1 # 自增1
# 保存文件
f.save(self.file_name)
# 判断文件是否存在
if not os.path.exists(self.file_name):
print("生成excel失败")
return False
print("生成excel成功")
return True
if __name__ == '__main__':
MysqlToExcel().generate_table()执行输出:
生成excel成功
查看excel表
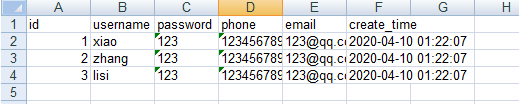
三、高级写法
在基础写法中,需要指定表的字段,比如:['id','username','password','phone','email']
如果一个表有70个字段怎么办?一个写笔记耗时间,能不能动态获取表字段呢?答案是可以的。
由于我在创建游标时,指定了pymysql.cursors.DictCursor,它返回的每一行数据,都是一个字典。
因此,通过dict.keys()就可以获取表字段了。
另外,我还得将查询结构中非string的转换为string类型。
test_excel.py
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# coding: utf-8
import os
import xlwt
import pymysql
import datetime
class MysqlToExcel(object):
def __init__(self):
self.host = '10.212.21.92'
self.user = 'root'
self.passwd = 'abcd1234'
self.db_name = 'test'
self.port = 3306
self.file_name = 'data.xls'
def get_query_results(self):
sql = "select * from test.users"
conn = pymysql.connect(
host=self.host,
user=self.user,
passwd=self.passwd,
port=self.port,
database=self.db_name,
charset='utf8',
cursorclass=pymysql.cursors.DictCursor
)
cur = conn.cursor() # 创建游标
cur.execute(sql) # 执行sql命令
result = cur.fetchall() # 获取执行的返回结果
# print(result)
cur.close()
conn.close() # 关闭mysql 连接
return result
def generate_table(self):
"""
生成excel表格
:return:
"""
# 删除已存在的文件
if os.path.exists(self.file_name):
os.remove(self.file_name)
result = self.get_query_results()
# print(result)
if not result:
print("查询结果为空")
return False
# 创建excel对象
f = xlwt.Workbook()
sheet1 = f.add_sheet('Sheet1', cell_overwrite_ok=True)
# 第一行结果
row0 = result[0]
# 列字段
column_names = list(row0)
# 写第一行,也就是列所在的行
for i in range(0, len(row0)):
sheet1.write(0, i, column_names[i])
# 写入多行
# 行坐标,从第2行开始,也是1
for row_id in range(1, len(result) + 1):
# 列坐标
for col_id in range(len(column_names)):
# 写入的值
value = result[row_id - 1][column_names[col_id]]
# 判断为日期时
if isinstance(value, datetime.datetime):
value = result[row_id - 1][column_names[col_id]].strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S')
# 写入表格
sheet1.write(row_id, col_id, value)
# 保存文件
f.save(self.file_name)
# 判断文件是否存在
if not os.path.exists(self.file_name):
print("生成excel失败")
return False
print("生成excel成功")
return True
if __name__ == '__main__':
MysqlToExcel().generate_table()执行脚本,结果同上!
四、自适应宽度
上面表格看着不美观,宽度没有自适应。
解决方法:
增加一个方法,获取宽度
def get_maxlength(self,value, col): """ 获取value最大占位长度,用于确定导出的xlsx文件的列宽 col : 表头,也参与比较,解决有时候表头过长的问题 """ # 长度列表 len_list = [] # 表头长度 width = 256 * (len(col) + 1) len_list.append(width) # 数据长度 if len(value) >= 10: width = 256 * (len(value) + 1) len_list.append(width) return max(len_list)
完整代码如下:
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# coding: utf-8
import os
import xlwt
import pymysql
import datetime
class MysqlToExcel(object):
def __init__(self):
self.host = '10.212.21.92'
self.user = 'root'
self.passwd = 'abcd1234'
self.db_name = 'test'
self.port = 3306
self.file_name = 'data.xls'
def get_query_results(self):
sql = "select * from test.users"
conn = pymysql.connect(
host=self.host,
user=self.user,
passwd=self.passwd,
port=self.port,
database=self.db_name,
charset='utf8',
cursorclass=pymysql.cursors.DictCursor
)
cur = conn.cursor() # 创建游标
cur.execute(sql) # 执行sql命令
result = cur.fetchall() # 获取执行的返回结果
# print(result)
cur.close()
conn.close() # 关闭mysql 连接
return result
def get_maxlength(self,value, col):
"""
获取value最大占位长度,用于确定导出的xlsx文件的列宽
col : 表头,也参与比较,解决有时候表头过长的问题
"""
# 长度列表
len_list = []
# 表头长度
width = 256 * (len(col) + 1)
len_list.append(width)
# 数据长度
if len(value) >= 10:
width = 256 * (len(value) + 1)
len_list.append(width)
return max(len_list)
def generate_table(self):
"""
生成excel表格
:return:
"""
# 删除已存在的文件
if os.path.exists(self.file_name):
os.remove(self.file_name)
result = self.get_query_results()
# print(result)
if not result:
print("查询结果为空")
return False
# 创建excel对象
f = xlwt.Workbook()
sheet1 = f.add_sheet('Sheet1', cell_overwrite_ok=True)
# 第一行结果
row0 = result[0]
# 列字段
column_names = list(row0)
# 写第一行,也就是列所在的行
for i in range(0, len(row0)):
sheet1.write(0, i, column_names[i])
# 写入多行
# 行坐标,从第2行开始,也是1
for row_id in range(1, len(result) + 1):
# 列坐标
for col_id in range(len(column_names)):
# 写入的值
value = result[row_id - 1][column_names[col_id]]
# 判断为日期时
if isinstance(value, datetime.datetime):
value = result[row_id - 1][column_names[col_id]].strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S')
# 获取表格对象
col = sheet1.col(col_id)
if value:
if isinstance(value, int):
value = str(value)
# 获取宽度
width = self.get_maxlength(value,column_names[col_id])
# 设置宽度
col.width = width
# 写入表格
sheet1.write(row_id, col_id, value)
# 保存文件
f.save(self.file_name)
# 判断文件是否存在
if not os.path.exists(self.file_name):
print("生成excel失败")
return False
print("生成excel成功")
return True
if __name__ == '__main__':
MysqlToExcel().generate_table()执行脚本,查看excel
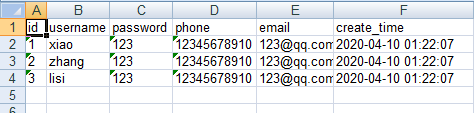
这样看着,就比较舒服了。
本文参考链接:
https://blog.csdn.net/baidu_41743195/article/details/103001210
https://blog.csdn.net/dl1456074580/article/details/87364999
- openvpn linux客户端使用
52230
- H3C基本命令大全
52150
- openvpn windows客户端使用
42298
- H3C IRF原理及 配置
39168
- Python exit()函数
33666
- openvpn mac客户端使用
30621
- python全系列官方中文文档
29319
- python 获取网卡实时流量
24284
- 1.常用turtle功能函数
24172
- python 获取Linux和Windows硬件信息
22542
- LangChain 1.0-Agent中间件-实现闭环(批准-编辑-拒绝动作)
124°
- LangChain 1.0-Agent中间件-汇总消息
124°
- LangChain 1.0-Agent中间件-删除消息
134°
- LangChain 1.0-Agent中间件-消息压缩
125°
- LangChain 1.0-Agent中间件-多模型动态选择
180°
- LangChain1.0-Agent-部署/上线(开发人员必备)
341°
- LangChain1.0-Agent-Spider实战(爬虫函数替代API接口)
381°
- LangChain1.0-Agent(进阶)本地模型+Playwright实现网页自动化操作
385°
- LangChain1.0-Agent记忆管理
362°
- LangChain1.0-Agent接入自定义工具与React循环
400°
- 姓名:Run
- 职业:谜
- 邮箱:383697894@qq.com
- 定位:上海 · 松江
