python编写mysql类实现mysq
发布时间:2019-09-08 09:09:46编辑:auto阅读(2281)
前言
我们都知道利用python实现mysql的操作是件很简单的事情,只需要熟练使用MySQLdb模块就能实现mysql的增删改查操作。
为了更好地整合mysql的操作,使用python的类讲mysql的操作整合到一起,是个不错的思路。这里我编写了一个简单的class,来实现对mysql的操作与查询。
操作
本例中,我们准备在mysql的iceny中创建了一张测试表t1,字段为id和timestamp,主要存储系统的时间戳,并在该表中进行增、删、改、查的操作:
当前mysql的状态:
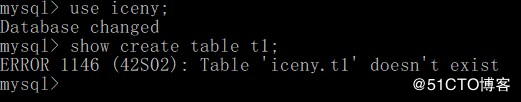
MySQLdb为python的第三方模块,使用之前需提前安装该模块,这里推荐pip安装:
pip install MySQL-python
注:python3.4之后Mysql-python已经不被支持了,可以换成mysqlclient模块。
编写mysql的class类:
#!/usr/local/env python3.6 # -*- coding: UTF-8 -*- import MySQLdb class Mysql(object): def __init__(self,host,port,user,passwd,db,charset='utf8'): """初始化mysql连接""" try: self.conn = MySQLdb.connect(host,user,passwd,db,int(port)) except MySQLdb.Error as e: errormsg = 'Cannot connect to server\nERROR(%s):%s' % (e.args[0],e.args[1]) print(errormsg) exit(2) self.cursor = self.conn.cursor() def exec(self,sql): """执行dml,ddl语句""" try: self.cursor.execute(sql) self.conn.commit() except: self.conn.rollback() def query(self,sql): """查询数据""" self.cursor.execute(sql) return self.cursor.fetchall() def __del__(self): """ 关闭mysql连接 """ self.conn.close() self.cursor.close()
创建mysql对象:
mysql_test = Mysql('192.168.232.128','3306','root','123456','iceny')创建表t1:
mysql_test.exec('create table t1 (id int auto_increment primary key,timestamp TIMESTAMP)') 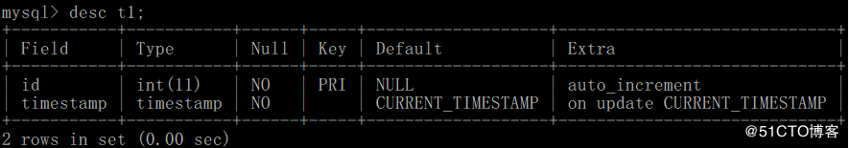
往t1插入一条数据:
mysql_test.exec('insert into t1 (id,timestamp) value (NULL,CURRENT_TIMESTAMP)') 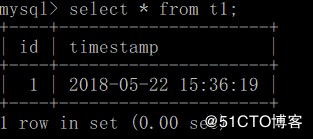
更新id为1的数据时间戳,改为执行当前的系统时间:
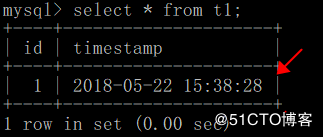
再插入一条数据,查询该表数据:
mysql_test.exec('insert into t1 (id,timestamp) value (NULL,CURRENT_TIMESTAMP)')
result = mysql_test.query('select * from t1')
print(result) 
可以看到查询出来的结果是存放在一个元祖中。
删除表中id = 1的数据:
mysql_test.exec('delete from t1 where id = 1') 
以上就是通过python编写简单的class类操作mysql增删改查的简单实现,这已经能够应付日常工作中大量的mysql操作了。
上一篇: 利用Python的pip命令安装nump
下一篇: Python:免安装的开发环境
- openvpn linux客户端使用
52216
- H3C基本命令大全
52121
- openvpn windows客户端使用
42286
- H3C IRF原理及 配置
39152
- Python exit()函数
33656
- openvpn mac客户端使用
30614
- python全系列官方中文文档
29297
- python 获取网卡实时流量
24275
- 1.常用turtle功能函数
24162
- python 获取Linux和Windows硬件信息
22529
- LangChain 1.0-Agent中间件-实现闭环(批准-编辑-拒绝动作)
100°
- LangChain 1.0-Agent中间件-汇总消息
104°
- LangChain 1.0-Agent中间件-删除消息
111°
- LangChain 1.0-Agent中间件-消息压缩
102°
- LangChain 1.0-Agent中间件-多模型动态选择
165°
- LangChain1.0-Agent-部署/上线(开发人员必备)
321°
- LangChain1.0-Agent-Spider实战(爬虫函数替代API接口)
365°
- LangChain1.0-Agent(进阶)本地模型+Playwright实现网页自动化操作
360°
- LangChain1.0-Agent记忆管理
338°
- LangChain1.0-Agent接入自定义工具与React循环
378°
- 姓名:Run
- 职业:谜
- 邮箱:383697894@qq.com
- 定位:上海 · 松江
