动手实践标签传播算法
复现论文:Learning with Local and Global Consistency1
lgc 算法可以参考:DecodePaper/notebook/lgc
初始化算法
载入一些必备的库:
from IPython.display import set_matplotlib_formats
%matplotlib inline
#set_matplotlib_formats('svg', 'pdf')
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from scipy.spatial.distance import cdist
from sklearn.datasets import make_moons
save_dir = '../data/images'创建一个简单的数据集
利用 make_moons 生成一个半月形数据集。
n = 800 # 样本数
n_labeled = 10 # 有标签样本数
X, Y = make_moons(n, shuffle=True, noise=0.1, random_state=1000)
X.shape, Y.shape((800, 2), (800,))def one_hot(Y, n_classes):
'''
对标签做 one_hot 编码
参数
=====
Y: 从 0 开始的标签
n_classes: 类别数
'''
out = Y[:, None] == np.arange(n_classes)
return out.astype(float)color = ['red' if l == 0 else 'blue' for l in Y]
plt.scatter(X[:, 0], X[:, 1], color=color)
plt.savefig(f"{save_dir}/bi_classification.pdf", format='pdf')
plt.show()
Y_input = np.concatenate((one_hot(Y[:n_labeled], 2), np.zeros((n-n_labeled, 2))))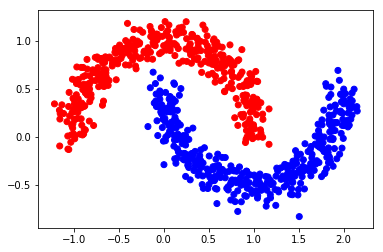
算法过程:
Step 1: 创建相似度矩阵 W
def rbf(x, sigma):
return np.exp((-x)/(2* sigma**2))sigma = 0.2
dm = cdist(X, X, 'euclidean')
vfunc = np.vectorize(rbf)
vfunc = np.vectorize(rbf)
W = vfunc(dm, sigma)
np.fill_diagonal(W, 0) # 对角线全为 0Step 2: 计算 S
\[ S = D^{-\frac{1}{2}} W D^{-\frac{1}{2}} \]
向量化编程:
def calculate_S(W):
d = np.sum(W, axis=1)
D_ = np.sqrt(d*d[:, np.newaxis]) # D_ 是 np.sqrt(np.dot(diag(D),diag(D)^T))
return np.divide(W, D_, where=D_ != 0)
S = calculate_S(W)迭代一次的结果
alpha = 0.99
F = np.dot(S, Y_input)*alpha + (1-alpha)*Y_input
Y_result = np.zeros_like(F)
Y_result[np.arange(len(F)), F.argmax(1)] = 1
Y_v = [1 if x == 0 else 0 for x in Y_result[0:,0]]
color = ['red' if l == 0 else 'blue' for l in Y_v]
plt.scatter(X[0:,0], X[0:,1], color=color)
#plt.savefig("iter_1.pdf", format='pdf')
plt.show()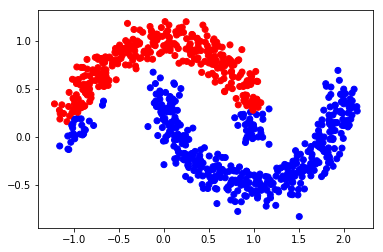
Step 3: 迭代 F "n_iter" 次直到收敛
n_iter = 150
F = Y_input
for t in range(n_iter):
F = np.dot(S, F)*alpha + (1-alpha)*Y_inputStep 4: 画出最终结果
Y_result = np.zeros_like(F)
Y_result[np.arange(len(F)), F.argmax(1)] = 1
Y_v = [1 if x == 0 else 0 for x in Y_result[0:,0]]
color = ['red' if l == 0 else 'blue' for l in Y_v]
plt.scatter(X[0:,0], X[0:,1], color=color)
#plt.savefig("iter_n.pdf", format='pdf')
plt.show()
from sklearn import metrics
print(metrics.classification_report(Y, F.argmax(1)))
acc = metrics.accuracy_score(Y, F.argmax(1))
print('准确度为',acc) precision recall f1-score support
0 1.00 0.86 0.92 400
1 0.88 1.00 0.93 400
micro avg 0.93 0.93 0.93 800
macro avg 0.94 0.93 0.93 800
weighted avg 0.94 0.93 0.93 800
准确度为 0.92875sklearn 实现 lgc
参考:https://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/label_propagation.html
在 sklearn 里提供了两个 lgc 模型:LabelPropagation 和 LabelSpreading,其中后者是前者的正则化形式。\(W\) 的计算方式提供了 rbf 与 knn。
-
rbf核由参数gamma控制(\(\gamma=\frac{1}{2{\sigma}^2}\)) -
knn核 由参数n_neighbors(近邻数)控制
def pred_lgc(X, Y, F, numLabels):
from sklearn import preprocessing
from sklearn.semi_supervised import LabelSpreading
cls = LabelSpreading(max_iter=150, kernel='rbf', gamma=0.003, alpha=.99)
# X.astype(float) 为了防止报错 "Numerical issues were encountered "
cls.fit(preprocessing.scale(X.astype(float)), F)
ind_unlabeled = np.arange(numLabels, len(X))
y_pred = cls.transduction_[ind_unlabeled]
y_true = Y[numLabels:].astype(y_pred.dtype)
return y_true, y_predY_input = np.concatenate((Y[:n_labeled], -np.ones(n-n_labeled)))
y_true, y_pred = pred_lgc(X, Y, Y_input, n_labeled)
print(metrics.classification_report(Y, F.argmax(1))) precision recall f1-score support
0 1.00 0.86 0.92 400
1 0.88 1.00 0.93 400
micro avg 0.93 0.93 0.93 800
macro avg 0.94 0.93 0.93 800
weighted avg 0.94 0.93 0.93 800networkx 实现 lgc
参考:networkx.algorithms.node_classification.lgc.local_and_global_consistency 具体的细节,我还没有研究!先放一个简单的例子:
G = nx.path_graph(4)
G.node[0]['label'] = 'A'
G.node[3]['label'] = 'B'
G.nodes(data=True)
G.edges()
predicted = node_classification.local_and_global_consistency(G)
predicted['A', 'A', 'B', 'B']更多精彩内容见:DecodePaper 觉得有用,记得给个 star !(@DecodePaper)
Zhou D, Bousquet O, Lal T N, et al. Learning with Local and Global Consistency[C]. neural information processing systems, 2003: 321-328.↩
