pygrametl的使用--python
发布时间:2019-09-22 08:09:12编辑:auto阅读(3053)
pygrametl是一个python的package用于ETL(Extract-Transform-Load )
简例
import MySQLdb
from pygrametl.datasources import SQLSource
conn = MySQLdb.connect(host="localhost", user="root", passwd="123456", db="ustcck", charset="utf8")
sql = "SELECT * FROM student;"
newnames = 'ID', 'Name', 'Gender'
resultsSource = SQLSource(connection=conn, query=sql, names=newnames)
print type(resultsSource)
for row in resultsSource:
print row
print row["Name"]
1.安装以及安装测试
$ pip install pygrametl
>>> import pygrametl
>>>
ok了!
2.pygrametl 支持多种数据源
'BackgroundSource', 'CSVSource', 'CrossTabbingSource', 'DictReader', 'DynamicForEachSource', 'FilteringSource', 'HashJoiningSource', 'JoiningSource', 'MergeJoiningSource', 'Process', 'ProcessSource', 'Queue', 'RoundRobinSource', 'SQLSource', 'TransformingSource',
'TypedCSVSource', 'UnionSource'..........
如:
(1)
import psycopg2
import pygrametl
from pygrametl.datasources import SQLSource
conn = psycopg2.connect(database="db", user="dbuser", password="dbpass")
sql = "SELECT * FROM table;"
resultsSource = SQLSource(connection=conn, query=sql)
(2)
import pygrametl
from pygrametl.datasources import CSVSource
resultsSource = CSVSource(csvfile=open('ResultsFile.csv', 'r', 16384), delimiter=',')
3.Dimension(维度)
pygrametl 提供了数据仓库维度交互,提供了一个在table中执行增删改查操作的接口。
使用Dimension两步走:
(1)创建ConnectionWrapper
(2)必须指定table的名字,key以及表中其他的列
下面是一个使用Dimension将相应的数据的插入到对应维度的操作的例子:(假设table已经存在,维度有'productid', 'name', 'category', 'price')
import psycopg2
import pygrametl
from pygrametl.tables import Dimension
products = [
{'name' : 'Calvin and Hobbes 1', 'category' : 'Comic', 'price' : '10'},
{'name' : 'Calvin and Hobbes 2', 'category' : 'Comic', 'price' : '10'},
{'name' : 'Calvin and Hobbes 3', 'category' : 'Comic', 'price' : '10'},
{'name' : 'Cake and Me', 'category' : 'Cookbook', 'price' : '15'},
{'name' : 'French Cooking', 'category' : 'Cookbook', 'price' : '50'},
{'name' : 'Sushi', 'category' : 'Cookbook', 'price' : '30'},
{'name' : 'Nineteen Eighty-Four', 'category' : 'Novel', 'price' : '15'},
{'name' : 'The Lord of the Rings', 'category' : 'Novel', 'price' : '60'}
]
pgconn = psycopg2.connect("""host='localhost' dbname='dw' user='dwuser'
password='dwpass'""")
conn = pygrametl.ConnectionWrapper(connection=pgconn)
productDimension = Dimension(
name='product',
key='productid',
attributes=['name', 'category', 'price'],
lookupatts=['name'])
for row in products:
productDimension.insert(row)
conn.commit()
conn.close()
4.FactTable。给个例子你就知道了
例:
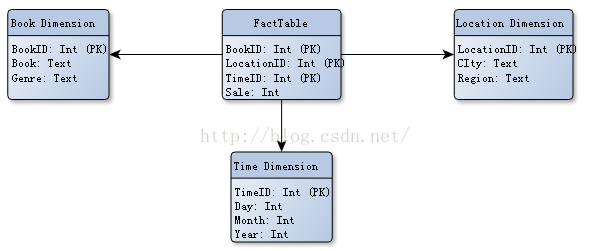
三步走:
(1)建立一个connection
(2)创建一个ConnectionWrapper实例
(3)创建 FactTable
import MySQLdb
import pygrametl
from pygrametl.tables import FactTable
conn = MySQLdb.connect(host="localhost", user="root", passwd="123", db="ustcck", charset="utf8")
conn = pygrametl.ConnectionWrapper(connection=conn)
factTable = FactTable(
name='facttable',
measures=['price'],
keyrefs=['storeid', 'productid', 'dateid'])
# A list of facts are ready to inserted into the fact table
facts = [{'storeid': 1, 'productid': 13, 'dateid': 4, 'price': 50},
{'storeid': 2, 'productid': 7, 'dateid': 4, 'price': 75},
{'storeid': 1, 'productid': 7, 'dateid': 4, 'price': 50},
{'storeid': 3, 'productid': 9, 'dateid': 4, 'price': 25}]
# The facts can be inserted using the insert method, before committing to DB
for row in facts:
factTable.insert(row)
conn.commit()
# Lookup retunes all both keys and measures given only the keys
factTable.lookup({'storeid': 1, 'productid': 13, 'dateid': 4})
# If a set of facts contain facts already existing in the database can the
# ensure method be used instead of calling lookup and insert manually, we
# also rename 'itemid' to 'productid' using the name mapping feature
newFacts = [{'storeid': 2, 'itemid': 7, 'dateid': 4, 'price': 75},
{'storeid': 1, 'itemid': 7, 'dateid': 4, 'price': 50},
{'storeid': 1, 'itemid': 2, 'dateid': 7, 'price': 150},
{'storeid': 3, 'itemid': 3, 'dateid': 6, 'price': 100}]
for row in newFacts:
# The second argument forces FactTable.ensure to not only match the keys
# for facts to be considered equal, but also checks if the measures are
# the same for facts with the same key, and if not raises a ValueError
factTable.ensure(row, True, {'productid': 'itemid'})
conn.commit()
conn.close()
5.Bulk Loading(大面积载入数据)
三个类可以用于Bulk Loading: BulkDimension, BulkFactTable, and CachedBulkDimension
#MySQLdb
def mysqlbulkloader(name, attributes, fieldsep, rowsep, nullval, filehandle):
global connection
cursor = connection.cursor()
sql = "LOAD DATA LOCAL INFILE '%s' INTO TABLE %s FIELDS TERMINATED BY '%s' LINES TERMINATED BY '%s' (%s);" % \
(filehandle, name, fieldsep, rowsep, ', '.join(attributes))
cursor.execute(sql)
参数含义:Parameters
name – 表名
attributes –属性序列列表
fieldsep – 属性分隔符
rowsep – row分隔符
nullval – null的替代
filehandle – 文件名或者文件对象
上一篇: python 常用类库!
下一篇: 【Python】Python中如何实现f
- openvpn linux客户端使用
52236
- H3C基本命令大全
52152
- openvpn windows客户端使用
42300
- H3C IRF原理及 配置
39175
- Python exit()函数
33667
- openvpn mac客户端使用
30621
- python全系列官方中文文档
29324
- python 获取网卡实时流量
24288
- 1.常用turtle功能函数
24173
- python 获取Linux和Windows硬件信息
22542
- LangChain 1.0-Agent中间件-实现闭环(批准-编辑-拒绝动作)
126°
- LangChain 1.0-Agent中间件-汇总消息
129°
- LangChain 1.0-Agent中间件-删除消息
142°
- LangChain 1.0-Agent中间件-消息压缩
134°
- LangChain 1.0-Agent中间件-多模型动态选择
182°
- LangChain1.0-Agent-部署/上线(开发人员必备)
344°
- LangChain1.0-Agent-Spider实战(爬虫函数替代API接口)
391°
- LangChain1.0-Agent(进阶)本地模型+Playwright实现网页自动化操作
390°
- LangChain1.0-Agent记忆管理
367°
- LangChain1.0-Agent接入自定义工具与React循环
405°
- 姓名:Run
- 职业:谜
- 邮箱:383697894@qq.com
- 定位:上海 · 松江
