Python编程入门(一)
发布时间:2019-09-22 07:40:18编辑:auto阅读(2351)
如php,perl,python,java等为脚本编程语言,通常需要通过解释器解释运行。
source code(源码 .py)--->conplier(编译)--->bytecode(字节码 .pyc)--->解释器pvm或者jvm(运行在各自的虚拟机,也是运行时的真正所在位置)--->processor(CPU)
原始,标准的实现方式
用于于java语言集成的实现
用于于.NET框架集成实现
过程式编程:指令+数据。以指令为中心,数据服务于指令需要。
对象式编程:以数据为中心(对象),指令服务于数据。
属性:
方法:
数值:
字符串:
列表:
字典:
元组:
文件:
其他类型:集合,类类型,None,布尔型
支持动态绑定
严格区分数据类型
可以显示的将一种数据类型转换为另一种数据类型,如:str(),repr(),format()等
整数
浮点数
复数
字符串字面量:用于引用一个字符序列,由特定次序的字符组成的字符序列。
支持3中引号:‘’,"","""(表示多行引用)
通过某种方式(例如对元素进行编号)组织在一起的数据元素的集合,这些数据元素可以是数字或者字符,甚至可以是其他数据结构;
Python的最基本数据结构是序列(有序的元素集合);
序列中的每个元素被分配一个序号——即元素的位置,也称为索引(索引从0开始编号);
Python 包含6种内建的数据序列:列表,元祖,字符串,Unicode字符串,buffer对象和xrange对象。
基本数据类型;
对象引用;
组合数据类型;
逻辑操作符;
控制流语句;
算数操作符;
输入/输出;
函数的创建与调用。
任何程序语言都必须能够表示基本数据项
Integral 类型
整型:不可变类型(如:-257,201624583337114373395836)
布尔型:True,False
浮点类型
浮点数:3.141592
复数:3+6j
十进制数:
字符串
如:'GNU is Not Unix',"hello","world"
Python将所有数据存为内存对象
Python中,变量事实上是指内存对象的引用;
动态类型:在任何时刻,只要需要,某个对象引用都可以重新引用一个不同的对象(可以是不同的数据类型);
内建函数type()用于返回给定数数据项的数据类型;
“=”用于将变量名于内存中的某对象绑定:如果对象事先存在,就直接进行绑定,否则,则由“=”创建引用的对象
只能包含字母,数字和下划线,且不能以数字开头;
区分字母大小写;
禁止使用保留字(Python2于Python3的保留字有所不同)
以单一下划线开头变量名(_x)不会被 from module import * 语句导入;
前后有下划线的变量名(_x_)是系统定义的变量名,对Python解释器有特殊意义;
以两个下划线开头但结尾没有下划线的变量名(__x)是类的本地变量;
交互式模式下,变量名"_"用于保存最后表达式的结果
python的此类包含了一系列预编写好的语句的程序文件称作“模块”;
能够直接运行的模块文件通常称作脚本(即程序的顶层文件)
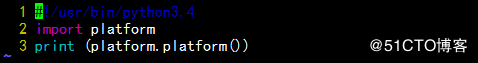
第一行为shebang,即执行脚本时,通知内容要启动的解释器;
第二行通过 import 导入一个python模块 platform
第三行打印platform模块的 platform 方法的执行结果
表达式是“某事”,而语句是“做某事(即指令)”;例如:3+4是某事,而 print(3+4) 是做某事;
语句的特性:它改变了事物,例如,赋值语句改变了变量,print 语句改变了屏幕输出等
标准 Python 环境提供
Python编程入门(一)
=========================================================================================
概述:
=========================================================================================
编程语言
1.脚本编程语言
★脚本编程语言
★python(java)程序的执行过程
2.Python的实现(pvm:编译器和解释器)
★CPython
★Jython
★IronPython
Python安装及数据类型
1.python:一切皆对象
★python2 <--> python3
☉类--->class有两部分组成
对象:向属性赋值;(python 当中一切皆对象!所以,一旦创建了一个对象,那么它就跟某类操作绑定起来了)
比如,对于数据类型“数值”来讲,它的属性就是:附一个数值,如,b=345。一旦对象类型确定了,那么它所支持的方法也就确定了,所以,任何一个对象只要创建出来,它必须属于某一个类型,也就必须跟这个类型支持的方法绑定在了一起(即:它所支持的方法也就确定了)
注意:
如果需要大量调用系统命令(如,系统维护脚本)来完成某些操作,用bash shell脚本足以实现;只有写一个完整的不依赖系统命令(如,复杂的程序)的情况下才有必要用到Python。
★python是动态类型的编程语言
☉变量
☉数据类型
◆核心数据类型
◆动态类型
◆强类型
★数字类型
★字符类型
演示:
1.python3的安装及位置查看
#安装python3
[root@CentOS6 ~]# yum install python34 python34-devel python34-libs python34-tools
#查看安装的位置
[root@CentOS6 ~]# rpm -ql python34
/usr/bin/pydoc3
/usr/bin/pydoc3.4
/usr/bin/python3
/usr/bin/python3.4
/usr/bin/python3.4m
/usr/bin/pyvenv
/usr/bin/pyvenv-3.4
/usr/share/doc/python34-3.4.5
/usr/share/doc/python34-3.4.5/LICENSE
/usr/share/doc/python34-3.4.5/README
/usr/share/man/man1/python3.1.gz
/usr/share/man/man1/python3.4.1.gz
[root@CentOS6 ~]# cd /usr/bin/
[root@CentOS6 bin]# ll python*
-rwxr-xr-x 2 root root 9032 Jul 24 2015 python
lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 6 Nov 6 2016 python2 -> python
-rwxr-xr-x 2 root root 9032 Jul 24 2015 python2.6
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 9 Jan 16 20:02 python3 -> python3.4
-rwxr-xr-x 2 root root 6088 Dec 12 00:59 python3.4
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 17 Jan 16 20:02 python3.4-config -> python3.4m-config
-rwxr-xr-x 2 root root 6088 Dec 12 00:59 python3.4m
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 173 Dec 12 00:58 python3.4m-config
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 3285 Dec 12 00:57 python3.4m-x86_64-config
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 16 Jan 16 20:02 python3-config -> python3.4-config
[root@CentOS6 ~]# python3
Python 3.4.5 (default, Dec 11 2017, 16:57:19)
[GCC 4.4.7 20120313 (Red Hat 4.4.7-18)] on linux
Type "help", "copyright", "credits" or "license" for more information.
>>> print("Hello,world") #在python3中,print为函数
Hello,world
>>> exit()2.字符串
[root@CentOS6 ~]# python3
Python 3.4.5 (default, Dec 11 2017, 16:57:19)
[GCC 4.4.7 20120313 (Red Hat 4.4.7-18)] on linux
Type "help", "copyright", "credits" or "license" for more information.
>>> str. #字符窜的常用操作
str.__add__( str.__getattribute__( str.__name__ str.__text_signature__ str.isdigit( str.rfind(
str.__base__( str.__getitem__( str.__ne__( str.__weakrefoffset__ str.isidentifier( str.rindex(
str.__bases__ str.__getnewargs__( str.__new__( str.capitalize( str.islower( str.rjust(
str.__basicsize__ str.__gt__( str.__prepare__( str.casefold( str.isnumeric( str.rpartition(
str.__call__( str.__hash__( str.__qualname__ str.center( str.isprintable( str.rsplit(
str.__class__( str.__init__( str.__reduce__( str.count( str.isspace( str.rstrip(
str.__contains__( str.__instancecheck__( str.__reduce_ex__( str.encode( str.istitle( str.split(
str.__delattr__( str.__itemsize__ str.__repr__( str.endswith( str.isupper( str.splitlines(
str.__dict__ str.__iter__( str.__rmod__( str.expandtabs( str.join( str.startswith(
str.__dictoffset__ str.__le__( str.__rmul__( str.find( str.ljust( str.strip(
str.__dir__( str.__len__( str.__setattr__( str.format( str.lower( str.swapcase(
str.__doc__ str.__lt__( str.__sizeof__( str.format_map( str.lstrip( str.title(
str.__eq__( str.__mod__( str.__str__( str.index( str.maketrans( str.translate(
str.__flags__ str.__module__ str.__subclasscheck__( str.isalnum( str.mro( str.upper(
str.__format__( str.__mro__ str.__subclasses__( str.isalpha( str.partition( str.zfill(
str.__ge__( str.__mul__( str.__subclasshook__( str.isdecimal( str.replace(
>>> mystr="Hello World"
>>> mystr1="""abc #支持"""或者''' 3引号的多行引用
... efg"""
>>> print(mystr)
Hello World
>>> print(mystr1)
abc
efg
>>> s='Hello'
>>> s*5 #字符串可进行乘法运算
'HelloHelloHelloHelloHello'
>>> w=' world'
>>> s+w #字符串相加
'Hello world'
>>> len(s) #取字符串的长度
5
>>> len(w)
6
>>> 'he' in s #判断字符串的成员关系
False
>>> 'He' in s
True
>>> s.lower() #转换为小写
'hello'
>>> s.upper() #转换为大写
'HELLO'
>>> help(str.replace) #查看帮助
>>> print(s)
Hello
>>> s.replace("H","h")
'hello'Python过程型程序设计介绍
1.数据结构
★数据结构
2.Python的关键要素
★Python的关键要素
☉要素1:基本数据类型
◆Python的基本数据类型有:
☉要素2:对象引用(变量)
◆变量命名规则
◆命名惯例:
注意:变量名没有类型,对象才有
☉要素3:组合数据类型
编写,执行Python代码
1.交互式解释器
★直接启动python,其显示信息取决于程序版本及操作系统等
2.python程序文件
★交互式模式下的程序执行完成后难以再次运行;
★将编写的程序文件保存至文件(.py)中方便多次运行
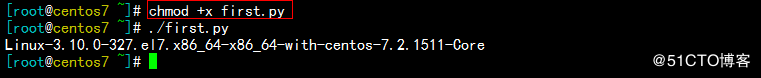
☉python源程序文件通常以 .py 为扩展名
☉给予此脚本执行权限,并执行即可
★Python程序可以分解成模块,语句,表达式和对象
☉程序由模块组成;
☉模块包含语句;
☉语句包含表达式
☉表达式建立并处理对象
演示:
1.platform模块
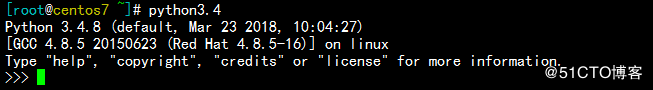
[root@centos7 ~]# python3.4
Python 3.4.8 (default, Mar 23 2018, 10:04:27)
[GCC 4.8.5 20150623 (Red Hat 4.8.5-16)] on linux
Type "help", "copyright", "credits" or "license" for more information.
>>> import platform
>>> platform.
platform.DEV_NULL platform.__spec__ platform.architecture(
platform._UNIXCONFDIR platform.__str__( platform.collections
platform._WIN32_CLIENT_RELEASES platform.__subclasshook__( platform.dist(
platform._WIN32_SERVER_RELEASES platform.__version__ platform.java_ver(
platform.__cached__ platform._default_architecture platform.libc_ver(
platform.__class__( platform._dist_try_harder( platform.linux_distribution(
platform.__copyright__ platform._follow_symlinks( platform.mac_ver(
platform.__delattr__( platform._get_real_winver( platform.machine(
platform.__dict__ platform._ironpython26_sys_version_parser platform.node(
platform.__dir__( platform._ironpython_sys_version_parser platform.os
platform.__doc__ platform._java_getprop( platform.platform(
platform.__eq__( platform._libc_search platform.popen(
platform.__file__ platform._lsb_release_version platform.processor(
platform.__format__( platform._mac_ver_xml( platform.python_branch(
platform.__ge__( platform._node( platform.python_build(
platform.__getattribute__( platform._norm_version( platform.python_compiler(
platform.__gt__( platform._parse_release_file( platform.python_implementation(
platform.__hash__( platform._platform( platform.python_revision(
platform.__init__( platform._platform_cache platform.python_version(
platform.__le__( platform._pypy_sys_version_parser platform.python_version_tuple(
platform.__loader__ platform._release_filename platform.re
platform.__lt__( platform._release_version platform.release(
platform.__name__ platform._supported_dists platform.subprocess
platform.__ne__( platform._sys_version( platform.sys
platform.__new__( platform._sys_version_cache platform.system(
platform.__package__ platform._sys_version_parser platform.system_alias(
platform.__reduce__( platform._syscmd_file( platform.uname(
platform.__reduce_ex__( platform._syscmd_uname( platform.uname_result(
platform.__repr__( platform._syscmd_ver( platform.version(
platform.__setattr__( platform._uname_cache platform.win32_ver(
platform.__sizeof__( platform._ver_output
>>> platform.platform()
'Linux-3.10.0-327.el7.x86_64-x86_64-with-centos-7.2.1511-Core'
>>> platform.uname()
uname_result(system='Linux', node='centos7', release='3.10.0-327.el7.x86_64', version='#1 SMP Thu Nov 19 22:10:57 UTC 2015', machine='x86_64', processor='x86_64')
>>> platform.system()
'Linux'
>>> platform.dist()
('centos', '7.2.1511', 'Core')
>>> platform.python_version()
'3.4.8'3.Python IDE
★IDLE
☉Eclipse和PyDev
☉PythonWin
☉Komodo
☉Wingware
☉PyCharm
上一篇: 使用python对redis操作
下一篇: python之协程
- openvpn linux客户端使用
52236
- H3C基本命令大全
52152
- openvpn windows客户端使用
42299
- H3C IRF原理及 配置
39171
- Python exit()函数
33667
- openvpn mac客户端使用
30621
- python全系列官方中文文档
29323
- python 获取网卡实时流量
24287
- 1.常用turtle功能函数
24172
- python 获取Linux和Windows硬件信息
22542
- LangChain 1.0-Agent中间件-实现闭环(批准-编辑-拒绝动作)
126°
- LangChain 1.0-Agent中间件-汇总消息
129°
- LangChain 1.0-Agent中间件-删除消息
142°
- LangChain 1.0-Agent中间件-消息压缩
134°
- LangChain 1.0-Agent中间件-多模型动态选择
182°
- LangChain1.0-Agent-部署/上线(开发人员必备)
344°
- LangChain1.0-Agent-Spider实战(爬虫函数替代API接口)
391°
- LangChain1.0-Agent(进阶)本地模型+Playwright实现网页自动化操作
390°
- LangChain1.0-Agent记忆管理
366°
- LangChain1.0-Agent接入自定义工具与React循环
405°
- 姓名:Run
- 职业:谜
- 邮箱:383697894@qq.com
- 定位:上海 · 松江