用python 判断一个单链表是否有环.
发布时间:2019-09-21 10:59:30编辑:auto阅读(2052)
用python 判断一个单链表是否有环.
https://leetcode.com/problems/linked-list-cycle/
思路1:
判断一个单链表是否有环,
可以用 set 存放每一个 节点, 这样每次 访问后把节点丢到这个集合里面.
其实 可以遍历这个单链表, 访问过后,
如果这个节点 不在 set 里面, 把这个节点放入到 set 集合里面.
如果这个节点在 set 里面 , 说明曾经访问过, 所以这个链表有重新 走到了这个节点, 因此一定有环
如果链表都走完了, 把所有的节点都放完了. 还是没有重复的节点, 那说明没有环.
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
@Time : 2019/1/12 00:59
@File : has_circle.py
@Author : frank.chang@shoufuyou.com
https://leetcode.com/problems/linked-list-cycle/
141. Linked List Cycle
Easy
1231
93
Favorite
Share
Given a linked list, determine if it has a cycle in it.
To represent a cycle in the given linked list,
we use an integer pos which represents the position (0-indexed) in the linked list where tail connects to.
If pos is -1, then there is no cycle in the linked list.
Example 1:
Input: head = [3,2,0,-4], pos = 1
Output: true
Explanation: There is a cycle in the linked list, where tail connects to the second node.
Example 2:
Input: head = [1,2], pos = 0
Output: true
Explanation: There is a cycle in the linked list, where tail connects to the first node.
Example 3:
Input: head = [1], pos = -1
Output: false
Explanation: There is no cycle in the linked list.
Follow up:
Can you solve it using O(1) (i.e. constant) memory?
Accepted
340,579
Submissions
971,443
"""
class LinkNode:
def __init__(self, value):
self.value = value
self.next = None
class Solution1:
"""
思路分析:
判断一个单链表是否有环,
可以用 set 存放每一个 节点, 这样每次 访问后把节点丢到这个集合里面.
其实 可以遍历这个单链表, 访问过后,
如果这个节点 不在 set 里面, 把这个节点放入到 set 集合里面.
如果这个节点在 set 里面 , 说明曾经访问过, 所以这个链表有重新 走到了这个节点, 因此一定有环.
如果链表都走完了, 把所有的节点都放完了. 还是没有重复的节点, 那说明没有环.
"""
def hasCycle(self, head):
mapping = set()
flag = False
p = head
while p:
if p not in mapping:
mapping.add(p)
else:
flag = True
break
p = p.next
return flag
还有一个解决方案:
定义 两个指针, 一个快指针fast, 一个慢指针slow, 快指针一次走两步,慢指针一次走一步.
如果 两个指针相遇了, 则说明链表是有环的.
如果 fast 都走到null了, 还没有相遇则说明没有环.
为什么是这样呢? 简单分析一下?

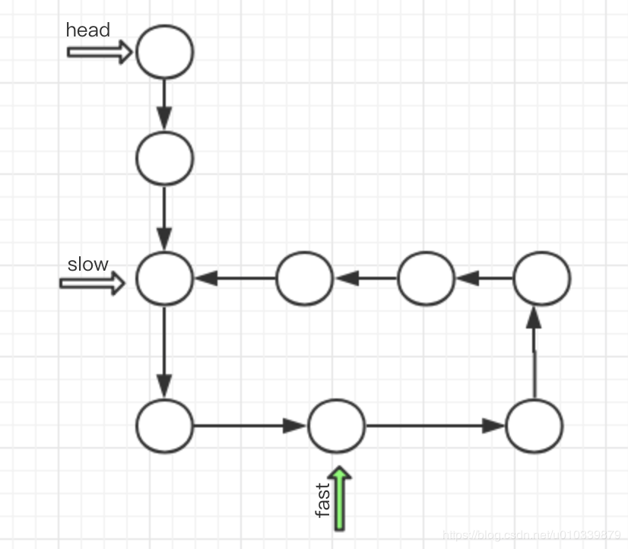
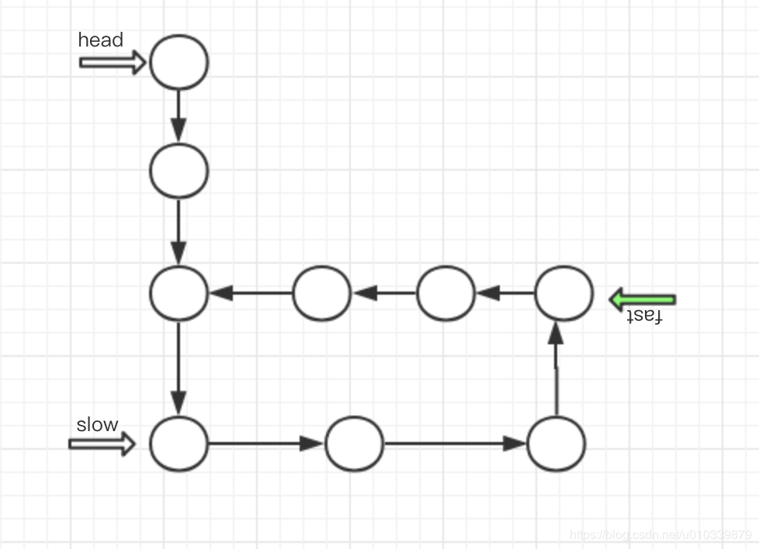
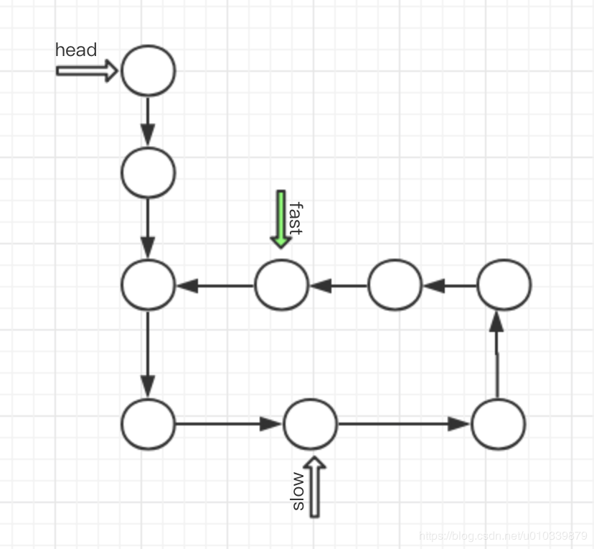
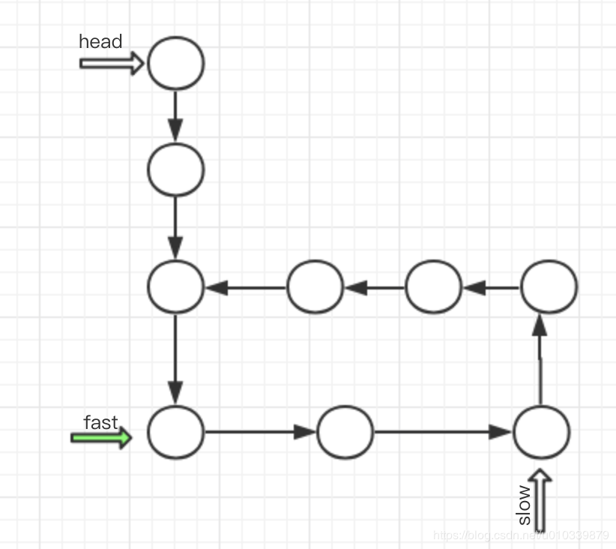
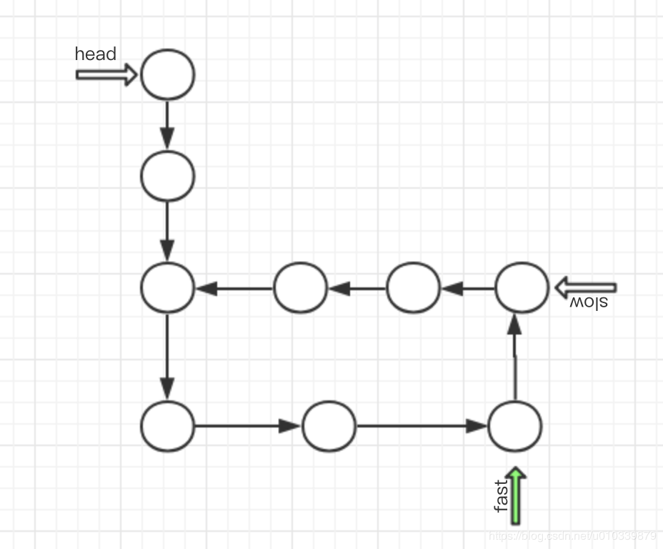
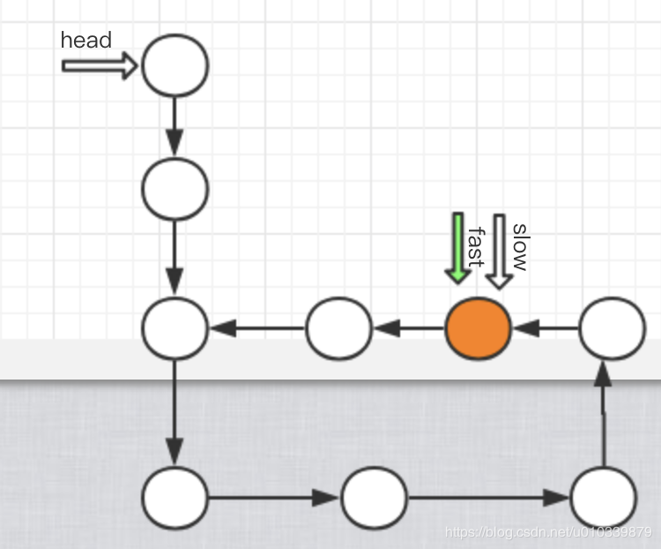
用图形来分析一下,这样可以清晰一点.
因为快指针 先走 所以快指针先进入环,之后慢指针后进入环, 无论如何,
最后 要么 慢指针进入环的时候, 快指针可能已经走了 很多遍环, 也有可能没有走完环. 但无论如何 当慢指针 进入环的时候,
fast 有可能在 慢指针的后面, 或者前面, 无论如何 快指针 是必慢指针走的快的 , 所以 只要有环 一定可以 和慢指针来一次相遇.
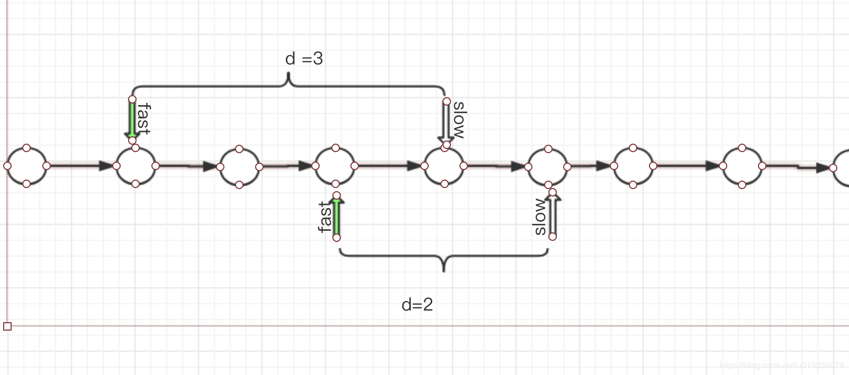
你可能想 会不会错过呢?
答案 是不会的. 你想 快指针一次 走两步, 慢指针一次都一步.
假设 这是一条无穷尽的单链表. 他们 每走一步, 两者之间的距离就减1, 所以 只要链表足够长, 是一定会相遇的.
看下图:
class Solution:
"""
定义 两个指针, 一个快指针fast, 一个慢指针slow, 快指针一次都两步,慢指针一次走一步.
如果 两个指针相遇了, 则说明链表是有环的.
如果 fast 都走到null了, 还没有相遇则说明没有环.
"""
def hasCycle(self, head):
flag = False
if head is None or head.next is None or head.next.next is None:
return flag
fast = head.next.next
slow = head.next
while fast is not slow:
if fast.next is None or fast.next.next is None:
# no circle
return flag
fast = fast.next.next
slow = slow.next
# 相遇肯定有环
if fast is slow:
# hasCircle
flag = True
return flag
if __name__ == '__main__':
pass
上一篇: python中程序运行计时的三种方式
下一篇: 2018年,10个最好用的Python集
- openvpn linux客户端使用
52231
- H3C基本命令大全
52152
- openvpn windows客户端使用
42298
- H3C IRF原理及 配置
39169
- Python exit()函数
33667
- openvpn mac客户端使用
30621
- python全系列官方中文文档
29323
- python 获取网卡实时流量
24286
- 1.常用turtle功能函数
24172
- python 获取Linux和Windows硬件信息
22542
- LangChain 1.0-Agent中间件-实现闭环(批准-编辑-拒绝动作)
126°
- LangChain 1.0-Agent中间件-汇总消息
129°
- LangChain 1.0-Agent中间件-删除消息
140°
- LangChain 1.0-Agent中间件-消息压缩
134°
- LangChain 1.0-Agent中间件-多模型动态选择
181°
- LangChain1.0-Agent-部署/上线(开发人员必备)
343°
- LangChain1.0-Agent-Spider实战(爬虫函数替代API接口)
388°
- LangChain1.0-Agent(进阶)本地模型+Playwright实现网页自动化操作
389°
- LangChain1.0-Agent记忆管理
364°
- LangChain1.0-Agent接入自定义工具与React循环
405°
- 姓名:Run
- 职业:谜
- 邮箱:383697894@qq.com
- 定位:上海 · 松江
