python_day16_pythom-
发布时间:2019-09-17 07:43:02编辑:auto阅读(2202)
16、py_mysql操作
pymysql 是python中操作mysql的模块,其使用方法和py2的mysqldb几乎相同
16.1、pymysql模块安装
1. pip install pymysql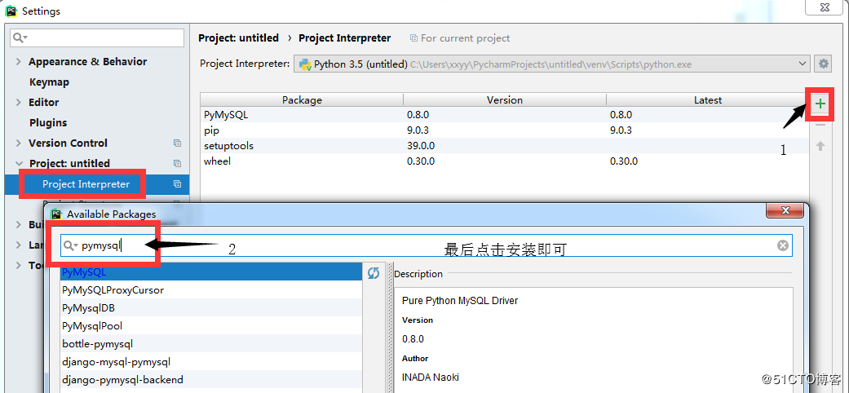
16.2、使用
16.2.1、导入模块
import pymysql
conn=pymysql.connect(host='127.0.0.1',port=3306,user='root',passwd='xiong',db='s1')
# 获取流标信息
cursor=conn.cursor()
ret=cursor.execute("select * from students")
print(ret) // 只会返回一共有多少行信息
# 操作见下方,每次操作完都需要提交,养成好习惯操作完就给连接关闭.
# 提交
conn.commit()
// 关闭连接以及游标
conn.close()
cursor.close()
2、SQL注入查询
SQL注入问题
1. SQL语句在程序中是字符串,动态拼接的字符串,拿用户输入的内容去拼接字符串
2. 不要自己拼接字符串
import pymysql
# mysql> create table userinfo(id int primary key auto_increment,user varchar(20) unique key, passwd varchar(20) );
# mysql> insert into userinfo (user,passwd) values ("xiong","123");
user = input("请输入用户名: ")
passwd = input("请输入密码: ")
conn = pymysql.connect(
host="127.0.0.1",
port=3306,
user="test",
password="test",
database="test",
charset="utf8",
)
# 获取光标
cursor = conn.cursor()
sql = "select * from userinfo where user=%s and passwd=%s"
ret = cursor.execute(sql, [user,passwd])
if ret:
print("登陆成功")
else:
print("登陆失败")
cursor.close()
conn.close()
提示: 如果sql是字符串拼接的,那么用户在输入名称 比如 xiong ' -- 执行时就会直接执行 select * from userinfo where user='xiong' 后面的and就会被注释,这样就能直接登陆成功,因为返回的直接为true
这里我们可以直接使用 pymysql execute让它自动拼接,避免因为用户输入而造成的SQL注入的问题
16.2.2、插入一个表
// 原生sql语句create table
sql_cmd="CREATE TABLE pysql(id INT PRIMARY KEY auto_increment,name VARCHAR (25))"
cursor.execute(sql_cmd)
# 查看mysql
MariaDB [s1]> show tables;
+--------------+
| Tables_in_s1 |
+--------------+
| pysql |
| students |
| teachers |
+--------------+
16.2.2.1、插入数据
// 原生sql语句 insert
insert_cmd="insert into pysql VALUES (1,'xiong1'),(2,'xiong2'),(3,'xiong3'),(4,'xiong4')"
cursor.execute(insert_cmd)
# 查看mysql
MariaDB [s1]> select * from pysql;
+----+--------+
| id | name |
+----+--------+
| 1 | xiong1 |
| 2 | xiong2 |
| 3 | xiong3 |
| 4 | xiong4 |
+----+--------+
4 rows in set (0.00 sec)16.2.2.2、lastrowid
获取插入数据库的最后一行的ID号
# 创建一个数据库
# MariaDB [(none)]> create database test;
# 创建一个标题表 包含标题名称跟ID号
# MariaDB [test]> create table title (id int primary key auto_increment, name varchar(20));
# 创建属性内容表 包含标题表的ID 作者消息 内容等
# MariaDB [test]> create table attribute (id int primary key auto_increment, name varchar(20), tid int);
import pymysql
conn = pymysql.connect(
host="127.0.0.1",
port=3306,
user="root",
password="xiong",
database="test",
charset="utf8"
)
# 光标位置
cursor = conn.cursor()
# sql
ti1 = "insert into title (name) values (%s)"
at1 = "insert into attribute (name,tid) values (%s,%s)"
cur1 = cursor.execute(ti1, 'hello world')
# 获取上面插入数据的ID
lastid = cursor.lastrowid
cur2 = cursor.execute(at1,["xiong",lastid])
# 增加操作 需要使用数据库建立的连接提交事务
conn.commit()
# 操作完之后,就关闭连接
cursor.close()
conn.close()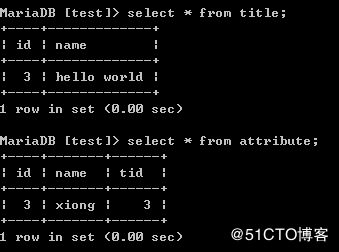
16.2.2.3、批量插入
# 新建一个用于批量增加数据的表
# MariaDB [test]> create table batchInsert (id int primary key auto_increment, name varchar(20), addr varchar(20));
import pymysql
conn = pymysql.connect(
host="127.0.0.1",
port=3306,
user="root",
password="xiong",
database="test",
charset="utf8"
)
cursor = conn.cursor()
sql = "insert into batchInsert (name,addr) values (%s,%s)"
# 这里需要可迭代的对象,必须是一个列表 或元组
tableList = [('xiong','sh'),("x2","bj"),("x3","hn")]
cursor.executemany(sql,tableList)
conn.commit()
cursor.close()
conn.close()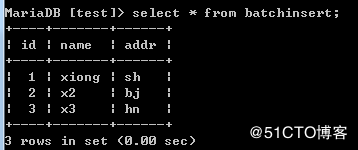
16.2.3、查看行数据
对象:fetchone, fetchall, fetchmany
# 需要先查询数据库,然后在进行查询数据库,如果没有先查,那么一定会报错,实测
**cursor.execute("select * from pysql")**
# 一次只查询一行
print(cursor.fetchone()) #(1, 'xiong1')
# fetchmany(nums) 选择一次查看多少行,
# 从第2行开始是因为流标现在就定在第二行的位置上
print(cursor.fetchmany(3)) # ((2, 'xiong2'), (3, 'xiong3'), (4, 'xiong4'))
# 查询所有的行 因为总行数只有4行 而流标已经到了最后一行了
print(cursor.fetchall()) #()
16.2.4、scroll
// 位置 relative (当前) ,absolute(起始)
# relative
print(cursor.fetchmany(2)) #((1, 'xiong1'), (2, 'xiong2'))
# 相对当前流标位置移动 从如上面游标已经在第2个了 +1就是第3个,打印下一条就是第4行数据
cursor.scroll(1,mode="relative")
print(cursor.fetchone()) # (4, 'xiong4')
# absloute
print(cursor.fetchmany(3)) # ((1, 'xiong1'), (2, 'xiong2'), (3, 'xiong3'))
# 从第1个开始,只能是正数,不能是负的.当前为1 +1也就是从第2个开始
cursor.scroll(1,mode="absolute")
print(cursor.fetchmany(2)) # ((2, 'xiong2'), (3, 'xiong3'))
16.2.5、字典形式查看
cursor=conn.cursor(cursor=pymysql.cursors.DictCursor) 设置成这个打印方式以字典形式展示
16.3 事务
16.3.1、sql事务
事务是指逻辑上的一组操作,组成这组操作的各个单元,要么全部成功,要么全部失败.
MariaDB [s1]> create table salary(id int primary key auto_increment,name varchar(30),sala double)
MariaDB [s1]> insert into salary values (1,'xiong',5555.55),(2,'yy',3333.33)
start TRANSACTION; --开启事务
-- 修改表,当事务没有commit的时候,数据是不会有所更改的
MariaDB [s1]> update salary set sala=sala-1000 where name='xiong';
-- 回退到上一次事务提前的时候,提交未存储的事务
MariaDB [s1]> rollback;
-- 保留点
MariaDB [s1]> savepoint
16.3.2、pymysql事务
自带事务功能,如果不提交commit那么修改也是无效的.
提交前的数据
MariaDB [s1]> select * from salary;
+----+-------+---------+
| id | name | sala |
+----+-------+---------+
| 1 | xiong | 3555.55 |
| 2 | yy | 6333.33 |
+----+-------+---------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
import pymysql
connect=pymysql.connect(host='127.0.0.1',port=3306,user='root',passwd='xiong',db='s1')
# 获取游标
curosr = connect.cursor()
try:
# 更新id1的总数,然后查询如果小于0就退出到Exception并回滚
curosr.execute("update salary set sala=sala-1000 WHERE id=1")
curosr.execute("select sala from salary where id=1")
if curosr.fetchall()[0][0] <0:
raise Exception
# 上面没有出错那么就更新这条就提交
curosr.execute("update salary set sala=sala+1000 WHERE id=2")
connect.commit()
except Exception:
connect.rollback()
connect.commit()
curosr.close()
connect.close()
修改之后的数据
MariaDB [s1]> select * from salary;
+----+-------+---------+
| id | name | sala |
+----+-------+---------+
| 1 | xiong | 2555.55 |
| 2 | yy | 7333.33 |
+----+-------+---------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
### 最后当小于1000的时候,在怎么提交也是会直接报错。
16.3.3、事务特性
原子性(Atomicity):原子性是指事务是一个不可分割的工作单位,事务中的操作要么都发生,要么都不发生。
一致性(Consistency):事务前后数据的完整性必须保持一致
隔离性(Isolation):事务的隔离性是指多个用户并发访问数据库时,一个用户的事务不能被其它用户的事务所干扰,多个并发事务之间数据要相互隔离
持久性(Durability):持久性是指一个事务一旦被提交,它对数据库中数据的改变就是永久性的,接下来即使数据库发生故障也不应该对其有任何影响
将数据库设计为串行化程的数据库,让一张表在同一时间内只能有一个线程来操作。如果将数据库设计为这样,那数据库的效率太低了。所以数据库的设计这没有直接将数据库设计为串行化,而是为数据库提供多个隔离级别选项,使数据库的使用者可以根据使用情况自己定义到底需要什么样的隔离级别。
四个隔离级别:
Serializable:可避免脏读、不可重复读、虚读情况的发生。(串行化)
Repeatable read:可避免脏读、不可重复读情况的发生。(可重复读)不可以避免虚读
Read committed:可避免脏读情况发生(读已提交)
Read uncommitted:最低级别,以上情况均无法保证。(读未提交)
安全性考虑:Serializable>Repeatable read>Read committed>Read uncommitted
数据库效率:Read uncommitted>Read committed>Repeatable read>Serializable
一般情况下,我们会使用Repeatable read、Read committed mysql数据库默认的数据库隔离级别Repeatable read
mysql中设置数据库的隔离级别语句:
set [global/session] transaction isolation level xxxx;
-- 查看隔离级别
MariaDB [s1]> select @@tx_isolation;
+-----------------+
| @@tx_isolation |
+-----------------+
| REPEATABLE-READ |
+-----------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
16.4、实例
有N个设备议器插入模拟数据, 时间必须不一致,页面中查询时需要
import pymysql
conn = pymysql.connect(host="10.1.1.1",port=3306,user="test",passwd="test",db="test")
cursor = conn.cursor()
import random,time
def system_time(start,end):
# 获取时间
time_range=random.randrange(start,end)
times=time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S",time.localtime(time_range))
return times
a=["s0000000001111000000000000000001","s0000000001111000000000000000003","00000001111100ff0000000111110001"]
# 循环每个议器,取出前12位,获取起始时间结束时间,然后插入到数据库中,最后一定要commit
alen = len(a)
for i in range(alen):
para_id = a[i]
rtu_cude = a[i][:12]
for i in range(1,1000):
COLLECT_TIME = system_time(1513000000, 1525000000)
SYSTEM_TIME = system_time(1533000000, 1533193884)
aaa = 'INSERT INTO `xx` (`top1`, `COLLECT_TIME`, `SYSTEM_TIME`, `cor_vlu`,`tco`) VALUES ("%s", "%s", "%s", "3175.46","%s")'%(para_id,COLLECT_TIME,SYSTEM_TIME,rtu_cude)
cursor.execute(aaa)
conn.commit()
上一篇: Python XML No module
下一篇: python二分查找法
- openvpn linux客户端使用
52230
- H3C基本命令大全
52150
- openvpn windows客户端使用
42298
- H3C IRF原理及 配置
39168
- Python exit()函数
33666
- openvpn mac客户端使用
30621
- python全系列官方中文文档
29319
- python 获取网卡实时流量
24284
- 1.常用turtle功能函数
24172
- python 获取Linux和Windows硬件信息
22542
- LangChain 1.0-Agent中间件-实现闭环(批准-编辑-拒绝动作)
124°
- LangChain 1.0-Agent中间件-汇总消息
124°
- LangChain 1.0-Agent中间件-删除消息
134°
- LangChain 1.0-Agent中间件-消息压缩
125°
- LangChain 1.0-Agent中间件-多模型动态选择
180°
- LangChain1.0-Agent-部署/上线(开发人员必备)
341°
- LangChain1.0-Agent-Spider实战(爬虫函数替代API接口)
382°
- LangChain1.0-Agent(进阶)本地模型+Playwright实现网页自动化操作
385°
- LangChain1.0-Agent记忆管理
362°
- LangChain1.0-Agent接入自定义工具与React循环
400°
- 姓名:Run
- 职业:谜
- 邮箱:383697894@qq.com
- 定位:上海 · 松江
