python 代码检查,实现行级代码优化
发布时间:2019-09-12 07:59:42编辑:auto阅读(2461)
有时候运行一个python程序,它需要运行很长时间。你或许想提升该程序的运行效率。那该怎么做那?
首先需要你要找到该程序瓶颈在哪里~ 比如,哪个函数的运行花费时间比较长? 哪个函数占用内存比较多,是否需要优化对内存的使用? 哪个占用cpu时间比较长? 等... 这些都需要考虑,python有几个库可以帮助你解决这些问题~ 废话不多说,切入主题。
首先写一段读取一个文件的python脚本:
touch c9.py
#!/usr/bin/env python
#Date: 2015/07/21
def read_file(fpath):
BLOCK_SIZE=1024
with open(fpath, 'rb') as fd:
block = fd.read(BLOCK_SIZE)
if block:
yield block
else:
return
def main():
for i in read_file('~/access.log')
print i
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()然后,对该代码进行测试。
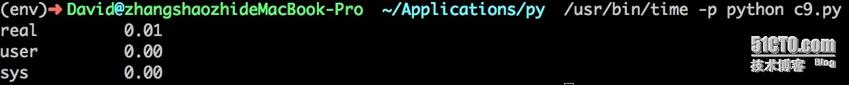
首先测试该代码运行时间:
它是一个外部的python测量。
real 表明了执行脚本花费的总时间。
user 表明了执行脚本花费在cpu的时间。
sys 表明了执行脚本花费在内核函数的时间。
因此, Real time和user+sys相加的不同或许表明了时间花费在等待i/o或者是系统在忙于执行其他任务。
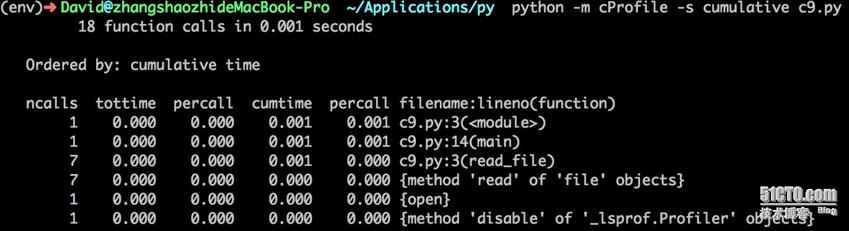
使用cProfile模块
如果想知道花费在每个函数和方法上的时间,以及他们被调用了多少次,你可以使用cProfile模块。
$ python -m cProfile -s cumulative + 要执行的python脚本 ( -s cumulative 它将通过累积花费在每个函数上的时间来排序)
你将看到花费在运行你的脚本总时间是比以前高的,这是我们测量每个函数执行时间的损失。
使用line_profile模块
line_profile 给出了在你代码美一行花费cpu时间。
首先需要安装line_profiler:
pip install line_profiler
接下来,你需要制定你想使用装饰器@profile评估哪个函数(你不需要把它import 到你的文件中) 
接下来测试该代码:
$ kernprof -l -v + 要执行的代码
-l 标识表明了逐行和-v标识表明详细输出。
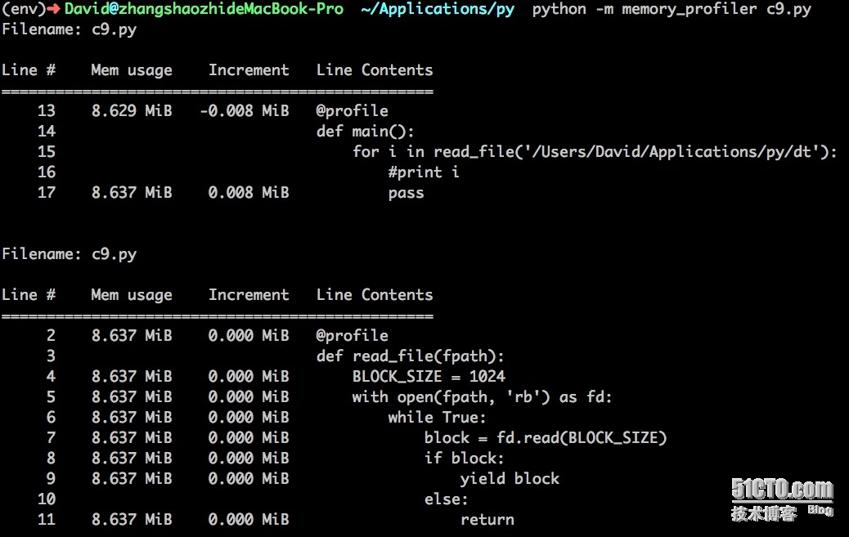
使用memory_profile模块
memory_profile模块被用于在逐行的基础上,测量你代码的内存使用率。尽管如此,它可能使得你的代码运行的更慢。
首先安装memory_profiler
$pip install memory_profiler
也建议安装psutil包,使得memory_profile模块运行的更快。
$ pip install psutil
类似于line_profile的方式,使用装饰器@profile来标记哪个函数被跟踪。
$python -m memory_profiler + 要执行的代码文件
看上面的输出,注意内存使用率的单位是MiB,这代表的是兆字节(1MiB = 1.05MB).
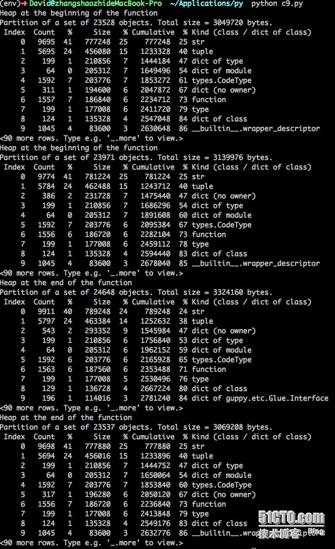
使用guppy模块
使用guppy模块你可以跟踪每个类型在你代码中每个阶段(字符、元组、字典等等)有多少对象被创建。
安装guppy:
$ pip install guppy
然后将你的代码该改成如下:
#!/usr/bin/env python
from guppy import hpy
def read_file(fpath):
hp = hpy()
print "Heap at the beginning of the function\n", hp.heap()
BLOCK_SIZE = 1024
with open(fpath, 'rb') as fd:
while True:
block = fd.read(BLOCK_SIZE)
if block:
yield block
else:
print "Heap at the end of the function\n", hp.heap()
return
def main():
hp = hpy()
print "Heap at the beginning of the function\n", hp.heap()
for i in read_file('/Users/David/Applications/py/dt'):
#print i
pass
print "Heap at the end of the function\n", hp.heap()
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()执行该代码:
$ python c9.py
通过数据结果,可以看出每个str、dict、function等对象被创建。
通过以上几个模块,可以更加清晰的了解python代码的执行过程以及对资源的占用情况。对代码优化有很大的帮助~~~
上一篇: python实现readline去掉换行
下一篇: python find()找多个相同子
- openvpn linux客户端使用
52216
- H3C基本命令大全
52124
- openvpn windows客户端使用
42289
- H3C IRF原理及 配置
39155
- Python exit()函数
33657
- openvpn mac客户端使用
30615
- python全系列官方中文文档
29300
- python 获取网卡实时流量
24275
- 1.常用turtle功能函数
24166
- python 获取Linux和Windows硬件信息
22529
- LangChain 1.0-Agent中间件-实现闭环(批准-编辑-拒绝动作)
106°
- LangChain 1.0-Agent中间件-汇总消息
106°
- LangChain 1.0-Agent中间件-删除消息
114°
- LangChain 1.0-Agent中间件-消息压缩
104°
- LangChain 1.0-Agent中间件-多模型动态选择
166°
- LangChain1.0-Agent-部署/上线(开发人员必备)
324°
- LangChain1.0-Agent-Spider实战(爬虫函数替代API接口)
365°
- LangChain1.0-Agent(进阶)本地模型+Playwright实现网页自动化操作
365°
- LangChain1.0-Agent记忆管理
342°
- LangChain1.0-Agent接入自定义工具与React循环
379°
- 姓名:Run
- 职业:谜
- 邮箱:383697894@qq.com
- 定位:上海 · 松江