用python 实现linux 的wc
发布时间:2019-09-10 09:17:23编辑:auto阅读(2046)
#!/usr/bin/env python
"""file name: opt_wc.py"""
import os
import sys
from optparse import OptionParser
def opt():
parser = OptionParser()
parser.add_option("-c", "--chars",
dest = "chars",
action = "store_true",
default = False,
help = "only count chars.")
parser.add_option("-w", "--words",
dest = "words",
action = "store_true",
default = False,
help = "only count words.")
parser.add_option("-l", "--lines",
dest = "lines",
action = "store_true",
default = False,
help = "only count lines.")
parser.add_option("-n", "--nototal",
dest = "nototal",
action = "store_true",
default = False,
help = "not print total count.")
options, args = parser.parse_args()
return options, args
def get_Count(data):
chars = len(data)
words = len(data.split())
lines = data.count('\n')
return lines, words, chars
def print_wc(options, lines, words, chars, fn):
if options.lines:
print lines,
if options.words:
print words,
if options.chars:
print chars,
print fn
def main():
options, args = opt()
if not (options.chars or options.words or options.lines):
options.chars, options.words, options.lines = True, True, True
if args:
total_lines, total_words, total_chars = 0, 0, 0
for fn in args:
if os.path.isfile(fn):
with open(fn) as fd:
data = fd.read()
lines, words, chars = get_Count(data)
print_wc(options, lines, words, chars, fn)
total_lines += lines
total_words += words
total_chars += chars
elif os.path.isdir(fn):
print >> sys.stderr, "%s: is a directory." % fn
else:
sys.stderr.write("%s: No such file or directory.\n" % fn)
if len(args) >1:
if not options.total:
print_wc(options, total_lines, total_words, total_chars, 'total')
else:
data = sys.stdin.read()
fn = ""
lines, words, chars = get_Count(data)
print_wc(options, lines, words, chars, fn)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()主要利用了optparse 里的OptionParser 模块,自定义选项。在这里,只定义了-l,-c,-w 三种命令,对应wc 命令的-l,-w,-c 三个命令,分别是统计行数,单词数和字符数。通过OptionParser 模块自定义的命令,python 版本的wc 命令也可以达到linux 命令wc 的效果。
optparse用法详解:
1. 创建OptionParser 对象,如 parser = OptionParser()
2. 调用parser 对象的add_option() 方法,自定义选项:
parser.add_option("-c",
"--chars",
dest = "chars",
action = "store_true",
default = False,
help = "only count chars.")
"-c"和"--chars"相当于短命令和长命令的区别。
dest 对象存储的值。
action 当解释到命令时会如何保存。一般有默认的三种情况,"store"、"store_true"、"stor_false":
当是"store"时,如果命令后还有值时,会将它保存在dest 声明的那个存储变量,例如<your_script> -c /etc/hosts; 则将"/etc/hosts"保存在chars 里。
当是"store_true"时,如果解释到-c 命令,则'chars' : True;
当是"store_false"时,如果解释到-c 命令,则'chars' : False;
default: action参数的默认取值
help: 相当于帮助信息
3. 当所有需要自定义的命令都已经准备好了,就可以调用parser.parse_args() 方法,这个方法返回两个值,options 和args 。
options 是一个字典dict的形式,这个字典的key 都是以上自定义的命令的dest值。例如,在这个例子里自定义了-c,-w,-l 三种命令选项,它们的action 都是"store_True",当输入有某一个命令时,它对应的存储变量的值就是True , 所以当以这种方式 python opt_wc.py -c 执行脚本的时候,就会获取到options 的值:['chars': True, 'words': Flase, 'lines': False].通过这个字典,就可以知道脚本要处理的命令是哪些了。
parser.parse_args()方法返回的第二个变量是args, 它是一个列表list,保存了命令行里除了-c,-l和--chars,--lines 这种短命令和长命令以外的参数值。例如命令行 python opt_wc.py -l /etc/hosts /etc/passwd ,那么args = ['/etc/hosts', '/etc/passwd'], 通过parse_args()方法返回的args 就可以知道脚本需要处理的文件。
扩展选项-n ,--nototal, 当在命令行输入-n 选项时,不再输出总数的统计。
python 脚本运行效果:
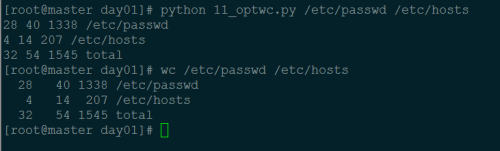
默认统计行数、字符数、单词数:
统计两个文件:
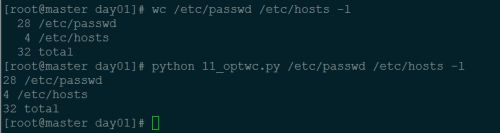
只统计行数:
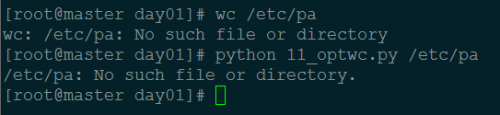
输出错误处理:
上一篇: python方式下自动登录51cto
下一篇: 安装redis及python redis
- openvpn linux客户端使用
52149
- H3C基本命令大全
52046
- openvpn windows客户端使用
42236
- H3C IRF原理及 配置
39083
- Python exit()函数
33597
- openvpn mac客户端使用
30552
- python全系列官方中文文档
29208
- python 获取网卡实时流量
24205
- 1.常用turtle功能函数
24105
- python 获取Linux和Windows硬件信息
22445
- LangChain1.0-Agent-部署/上线(开发人员必备)
248°
- LangChain1.0-Agent-Spider实战(爬虫函数替代API接口)
287°
- LangChain1.0-Agent(进阶)本地模型+Playwright实现网页自动化操作
294°
- LangChain1.0-Agent记忆管理
269°
- LangChain1.0-Agent接入自定义工具与React循环
306°
- LangChain1.0-Agent开发流程
276°
- LangChain1.0调用vllm本地部署qwen模型
307°
- LangChain-1.0入门实践-搭建流式响应的多轮问答机器人
311°
- LangChain-1.0入门实战-1
319°
- LangChain-1.0教程-(介绍,模型接入)
336°
- 姓名:Run
- 职业:谜
- 邮箱:383697894@qq.com
- 定位:上海 · 松江